“Chemically distinct liquid shooting up from the seafloor” has been detected by researchers on a stretch of a 600-mile-long fault line in the Pacific Ocean, which is situated only 50 miles away from the Oregon coast, and could potentially trigger a catastrophic earthquake in the Pacific Northwest.
"Newly Discovered Seafloor Seep" Off Oregon Coast On Fault Line May Be Harbinger To Major Quake https://t.co/AlZ9oesOuv
— zerohedge (@zerohedge) April 17, 2023
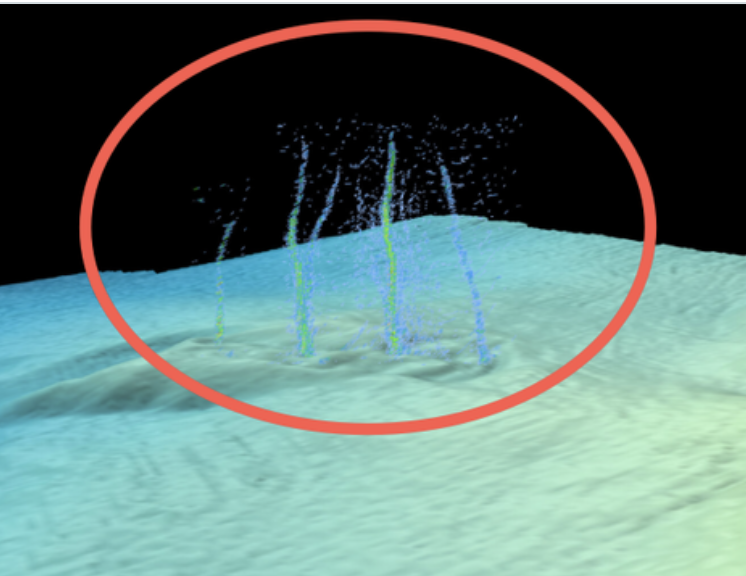
This sonar image of the Pythias Oasis site shows bubbles rising from the seafloor about two-thirds of a mile deep and 50 miles off Newport, Oregon. These bubbles are a byproduct of a unique site where warm, chemically distinct fluid gushes from the seafloor. Researchers believe this fluid comes directly from the Cascadia megathrust zone, or plate boundary, and helps control stress buildup between the two plates.
The field of plate tectonics is not that old, and scientists continue to learn the details of earthquake-producing geologic faults. The Cascadia Subduction Zone — the eerily quiet offshore fault that threatens to unleash a magnitude-9 earthquake in the Pacific Northwest — still holds many mysteries.
A study led by the University of Washington discovered seeps of warm, chemically distinct liquid shooting up from the seafloor about 50 miles off Newport, Oregon. The paper, published Jan. 25 in Science Advances, describes the unique underwater spring the researchers named Pythia’s Oasis. Observations suggest the spring is sourced from water 2.5 miles beneath the seafloor at the plate boundary, regulating stress on the offshore fault.
The team made the discovery during a weather-related delay for a cruise aboard the RV Thomas G. Thompson. The ship’s sonar showed unexpected plumes of bubbles about three-quarters of a mile beneath the ocean’s surface. Further exploration using an underwater robot revealed the bubbles were just a minor component of warm, chemically distinct fluid gushing from the seafloor sediment. WU
[Updated 4/18/2023 for clarification:
- Scientists are not alarmed at discovering this geologic feature, which does not trigger earthquakes but may regulate friction in the fault zone
- This discovery does not change the current risk of a large earthquake on the Cascadia Subduction Zone]